Face recognition is a computer vision technology that involves the automatic identification and verification of individuals based on their unique facial features.
Face recognition algorithms analyze facial patterns, such as the arrangement of eyes, nose, mouth, and other facial landmarks, to create a unique facial template or "faceprint" for each individual.
Face recognition algorithms analyze facial patterns, such as the arrangement of eyes, nose, mouth, and other facial landmarks, to create a unique facial template or "faceprint" for each individual.
How Face Recognition Works
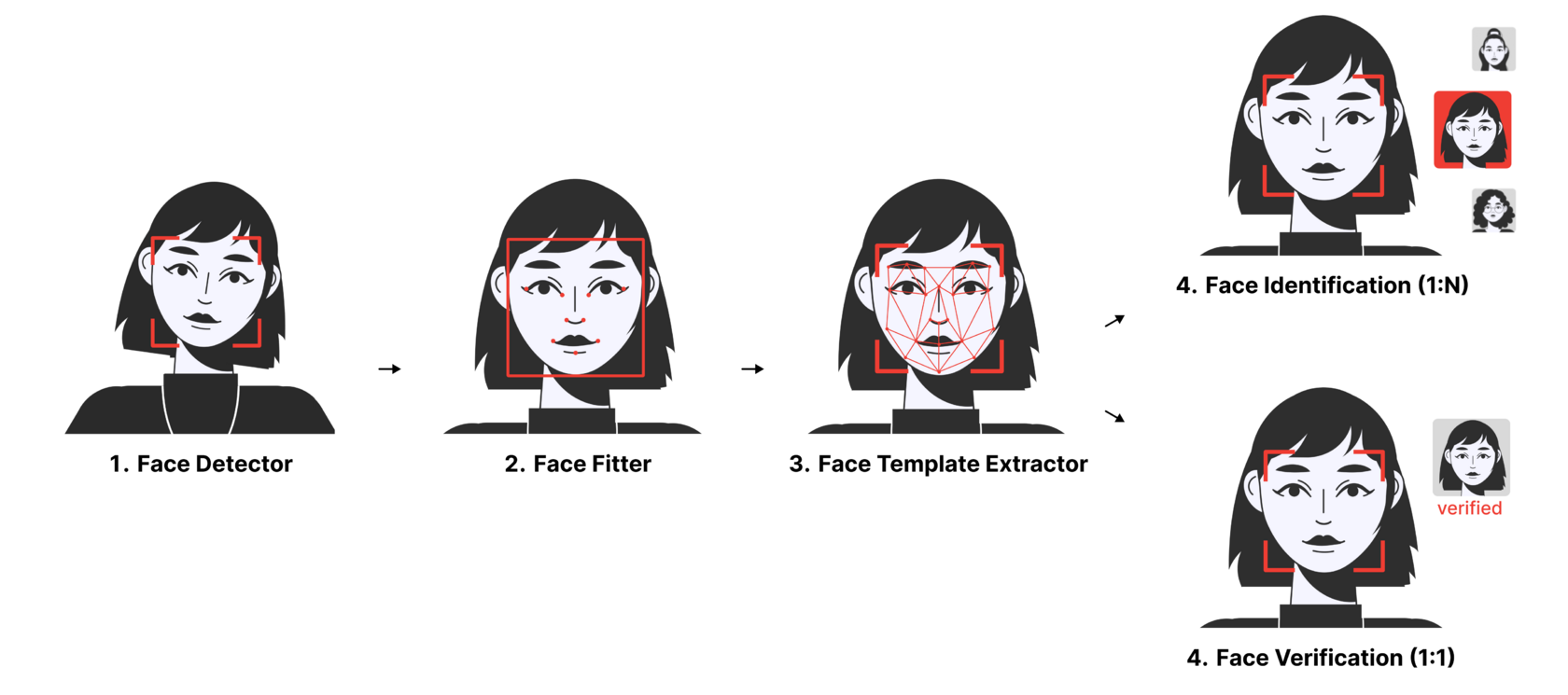
Face recognition technology typically follows a series of steps to identify and verify individuals based on their unique facial features. Here is a general overview of how it works:
Face Detection
The process begins with face detection, where an algorithm scans an image or video frame to locate and extract faces. Various techniques, such as Haar cascades, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), or deep learning models, can be used for this purpose.
Face Alignment and Landmark Detection
Once a face is detected, the algorithm identifies key facial landmarks or points, such as the position of the eyes, nose, mouth, and other facial features. This step helps normalize and align faces to a standard position, allowing for accurate comparisons and measurements.
Face Template Extraction
Next, the face recognition algorithm analyzes facial landmarks and extracts unique features that distinguish one face from another. These features can include the relative distances between facial landmarks, the shape of the eyes, the curvature of the lips, or other spatial relationships.
The extracted facial features are encoded into a mathematical representation or a feature vector. This encoding typically involves techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), or deep learning-based embeddings, such as FaceNet or VGGFace.
The extracted facial features are encoded into a mathematical representation or a feature vector. This encoding typically involves techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), or deep learning-based embeddings, such as FaceNet or VGGFace.
Face Matching
The encoded face features are then compared against a database of pre-existing face templates or faceprints. The database can contain faces of authorized individuals, suspects, or a larger dataset for identification purposes.
The comparison can be performed using various algorithms, such as Euclidean distance, cosine similarity, or neural network-based matching.
The algorithm determines the similarity or distance between the encoded face features and the faces in the database.
If a close match is found, it indicates a potential identification or verification. The algorithm can provide a confidence score or threshold to determine the level of similarity required for a positive match.
The comparison can be performed using various algorithms, such as Euclidean distance, cosine similarity, or neural network-based matching.
The algorithm determines the similarity or distance between the encoded face features and the faces in the database.
If a close match is found, it indicates a potential identification or verification. The algorithm can provide a confidence score or threshold to determine the level of similarity required for a positive match.
Based on the matching results and the set threshold, face recognition system makes a decision, such as confirming the identity of an individual, identifying an unknown person, or rejecting a mismatch.
Use Cases
Face recognition systems have a wide range of use cases across various industries and sectors. Here are some notable examples:
Public Safety 🏙️
Face recognition helps law enforcement identify suspects, find missing persons, and monitor public spaces for potential security threats. Agencies can analyze video surveillance footage and compare it against a database of known individuals to assist in investigations.
The technology is also utilized in smart city initiatives for traffic management, and crowd control. It can help identify individuals of interest in real-time, monitor public spaces, and optimize traffic flow in congested areas.
Identity Verification in Banking 🏦
Face recognition technology is used in authentication and identity verification processes for opening bank accounts, onboarding new customers for financial services, verification for online transactions, access to age-restricted content, and more.
Access Control and Attendance Tracking ⏱️
Face recognition is commonly used for access control systems, allowing authorized individuals to enter secure areas without the need for physical keys or access cards. It is used in industries such as airports, government facilities, corporate offices, and residential complexes to enhance security measures.
With face recognition systems employees can clock in and out by facing a camera, simplifying the payroll process. It also helps prevent time theft and provides insights into employee attendance patterns.
Retail and Marketing 🛒
Retailers employ face recognition to detect repeat shoplifters and analyze customer demographics, behaviors, and emotions. This data helps prevent theft losses and speed up investigations, personalize the shopping experience, improve targeted advertising campaigns, and track customer engagement within stores.
Face Recognition FAQs
How Accurate is Face Recognition?
The accuracy of face recognition technology can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the images or video frames, the algorithms and techniques used, and the specific application or use case. Here are some key points regarding the accuracy of face recognition:
- Facial Image Quality: The quality and clarity of the images or video frames used for face recognition greatly impact the accuracy of the system. High-resolution, well-lit, and properly aligned images generally yield better results than low-resolution, blurry, or poorly illuminated images. Face recognition algorithms can face challenges when dealing with variations in pose (e.g., different angles or orientations of the face) and facial expressions (e.g., smiling, frowning, or wearing glasses). Advanced algorithms and techniques, including deep learning models, have significantly improved the accuracy in handling these variations.
- Enrollment Process: Face recognition accuracy also depends on the quality and diversity of the images used during the enrollment process. A more comprehensive and representative set of images used for creating the initial face template or faceprint can enhance the system's ability to accurately match and identify individuals. The accuracy of face recognition has significantly improved in recent years due to advancements in computer vision techniques, particularly with the rise of deep learning models. Deep learning-based approaches, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and face embedding networks, have demonstrated higher accuracy rates in face recognition tasks.
- False Positives and False Negatives: Face recognition systems can sometimes produce false positives (incorrectly identifying a person) or false negatives (failing to identify a person correctly). The balance between minimizing false positives and false negatives can be adjusted by setting appropriate thresholds or confidence levels based on the specific requirements and use case.
- Application-Specific Factors: The accuracy of face recognition can also be influenced by the specific application or use case. For example, face recognition for access control in controlled environments (e.g., employee access to a secure building) tends to have higher accuracy compared to face recognition in uncontrolled and challenging environments (e.g., public spaces with varying lighting conditions and large crowds).
Is Face Recognition Safe?
Face recognition systems employ distinctive mathematical patterns to store biometric data, making them one of the most secure and efficient means of identification within the realm of biometric technology.
To mitigate the potential for unauthorized access, facial data can be anonymized and safeguarded to maintain privacy.
By incorporating liveness detection technology, these systems can differentiate between actual users and facial images, thereby preventing the system from being deceived by a photograph of a living individual.
To mitigate the potential for unauthorized access, facial data can be anonymized and safeguarded to maintain privacy.
By incorporating liveness detection technology, these systems can differentiate between actual users and facial images, thereby preventing the system from being deceived by a photograph of a living individual.
What is a Confidence Score in Face Recognition?
In face detection and comparison systems, confidence scores, also referred to as similarity scores, play a crucial role. They offer valuable insights into the degree of similarity between two images.
A higher confidence score indicates a greater likelihood that the two images correspond to the same individual. Thus, confidence scores utilize AI to determine the presence of a face in an image or establish a match with another face in a separate image.
Each prediction made by the face recognition system using AI is associated with a threshold score level that can be adjusted. Typically, automated matches are based on a high percentage, such as a confidence score above 99%.
Lower confidence scores may be utilized to explore the closest potential matches, which are then further assessed by a human investigator.
A higher confidence score indicates a greater likelihood that the two images correspond to the same individual. Thus, confidence scores utilize AI to determine the presence of a face in an image or establish a match with another face in a separate image.
Each prediction made by the face recognition system using AI is associated with a threshold score level that can be adjusted. Typically, automated matches are based on a high percentage, such as a confidence score above 99%.
Lower confidence scores may be utilized to explore the closest potential matches, which are then further assessed by a human investigator.
3DiVi’s top NIST-ranked solutions cover a full spectrum of face recognition needs, tailored for developers, businesses, and system integrators. Reach out to get the perfect fit for your project with expert guidance from our team.